Numb3rs 110: Dirty Bomb
In this episode there was a discussion about triangulation and there was
a scene where Charlie explains the prisoner's dilemma to three
prisoners in the hope that it will make one of them confess.
Triangulation
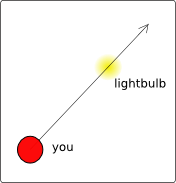 In this episode a truckload of radioactive waste has been hijacked
and Charlie uses triangulation of the radiation the waste emits
to find where it is. This is mathematically similar to trying to find a
lightbulb in a very large field (without moving). If you are standing in
a field, then you will be able to see the lightbulb but you won't be able
to tell how far away it is. This means you know that it lies somewhere
on a particular line that goes through you, which probably wouldn't be
particularly useful, since to find the lightbulb without gathering more
information you would have to walk along the entire line to get to the
lightbulb.
In this episode a truckload of radioactive waste has been hijacked
and Charlie uses triangulation of the radiation the waste emits
to find where it is. This is mathematically similar to trying to find a
lightbulb in a very large field (without moving). If you are standing in
a field, then you will be able to see the lightbulb but you won't be able
to tell how far away it is. This means you know that it lies somewhere
on a particular line that goes through you, which probably wouldn't be
particularly useful, since to find the lightbulb without gathering more
information you would have to walk along the entire line to get to the
lightbulb.
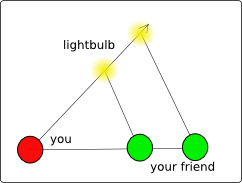 However, let's say you have a friend in the field and both
you and your friend have lightbulbs and radios. Then you can report to each
other the angle between the friend's lightbulb and the other lightbulb. Is
this enough to find the other lightbulb? Not quite, because there is no
angle-angle theorem in geometry. In other words, if you adapt coordinates
so that you are at the origin, then if you double the distances of the
other lightbulb and your friend from the origin, both the angles that you
and your friend measure will be the same. The only way to fix this is to
measure the distance between you and your friend.
However, let's say you have a friend in the field and both
you and your friend have lightbulbs and radios. Then you can report to each
other the angle between the friend's lightbulb and the other lightbulb. Is
this enough to find the other lightbulb? Not quite, because there is no
angle-angle theorem in geometry. In other words, if you adapt coordinates
so that you are at the origin, then if you double the distances of the
other lightbulb and your friend from the origin, both the angles that you
and your friend measure will be the same. The only way to fix this is to
measure the distance between you and your friend.
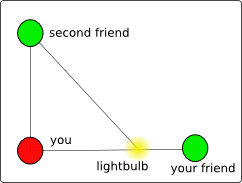 Of course, if you are unlucky there will be a problem with this. There's
a chance that the lightbulb will lie on the line between you and your friend.
If this is the case, it would be impossible for you and your friend to
tell where on the line the lightbulb is. This can be fixed, however, by adding
a third friend. If the three friends make sure they aren't all standing on
a single line, then they can always find the lightbulb.
Of course, if you are unlucky there will be a problem with this. There's
a chance that the lightbulb will lie on the line between you and your friend.
If this is the case, it would be impossible for you and your friend to
tell where on the line the lightbulb is. This can be fixed, however, by adding
a third friend. If the three friends make sure they aren't all standing on
a single line, then they can always find the lightbulb.
Activity 1:
Let's say you are standing on the coordinates (0,0) (the origin),
your first friend is standing at (1,0), and your second friend is standing
at (0,1). Also, assume the lightbulb is in the first quadrant so that
both its coordinates are positive.
- If the angle you see between your first friend and the lightbulb is
45 degrees and the angle he sees between you and the lightbulb is 90
degrees, where is the lightbulb?
- If both your friends report an angle of 90 degrees between you and the
lightbulb, where is the lightbulb?
- What if both your friends report an angle of 0 degrees between you
and the lightbulb?
The GPS, or
Global Positioning System, uses a similar method to determine the
exact location of a small handheld unit. Instead of having friends in a field
the system has satellites in the sky that have very precise clocks in them.
The handheld unit receives signals from the satellites saying what time
they think it is and their current location, which allows the handheld unit
to calculate the distance from it to each of the satellites. Then the
handheld unit is able to mathematically determine its location. Interestingly,
the clocks are so accurate that they are able to detect effects from
general relativity, and correcting for these effects leads to improvements
in positional measurement of tens of meters.
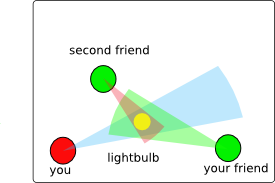
Activity 2 In the above picture with errors in
measurements, which friend would be better to ask about his estimate
of the angle between you and the lightbulb? Why? (Assume each friend has
the same error in measuring angles.)
The Prisoner's Dilemma
In this episode Charlie refers to the Prisoner's Dilemma, which is a particular
game that shows that if the players in a game are only looking out for
themselves and not colluding with the other players, then the results
of the game might be worse for everyone involved. Here's how it works.
Suppose that there are two prisoners that were involved in the same crime,
and for the police to successfully convict either one of them, they need
the testimony of the other one. If neither prisoner testifies, then they will
each serve 2 months on minor charges. If one testifies and the other doesn't,
then the testifier will go free and the other will serve 12 years. However,
if both testify, then each will get 8 years. Now it's obvious that if the
prisoners can collude and trust each other, neither will testify. This result
would be the best possible outcome in the sense that the total time served
would be minimized. However, if each prisoner only acts in his own interest,
both of them will testify. This is because if one prisoner testifies,
the outcome for him is better than if he didn't testify
no matter what the other person does.
This situation can be conveniently described in a table where the first
number listed is the incarceration time (called a payoff in game theory)
of the first prisoner and the second number is the incarceration time of
the second prisoner.
| Prisoner 2 Testifies | Prisoner 2 is Silent |
| Prisoner 1 Testifies | 8, 8 | 0, 12 |
| Prisoner 1 is Silent | 12, 0 | 2 months, 2 months |
Activity 3:
- If we have the following table, what are some conditions on the numbers
a, b, c, d so that the argument given above still works and the
equilbrium solution is the lower right hand square?
| Prisoner 2 Testifies | Prisoner 2 is Silent |
| Prisoner 1 Testifies | a, a | b, c |
| Prisoner 1 is Silent | c, b | d, d |
- Use reasoning similar to the argument above to figure out the
equilibrium choices for the following game. (The left number is the
payoff for player 1, and for this game bigger numbers are better.)
| Player 2 choice A | Player 2 choice B |
Player 2 choice C |
| Player 1 choice A | 4, 9 | 6, 4 | 1, 9 |
| Player 1 choice B | 5, 3 | 9, 5 | 5, 2 |
| Player 1 choice C | 1, 7 | 15, 12 | 10,8 |
- Will similar reasoning work for the following game? Why or why not?
Is there an equilibrium solution? (An equilibrium solution is a choice for
player A and B such that given knowledge of player B's choice, player A
wouldn't want to change his choice, and vice versa.)
| Prisoner 2 Testifies | Prisoner 2 is Silent |
| Prisoner 1 Testifies | 2, -2 | -2, 2 |
| Prisoner 1 is Silent | -2, 2 | 2, -2 |
 In this episode a truckload of radioactive waste has been hijacked
and Charlie uses triangulation of the radiation the waste emits
to find where it is. This is mathematically similar to trying to find a
lightbulb in a very large field (without moving). If you are standing in
a field, then you will be able to see the lightbulb but you won't be able
to tell how far away it is. This means you know that it lies somewhere
on a particular line that goes through you, which probably wouldn't be
particularly useful, since to find the lightbulb without gathering more
information you would have to walk along the entire line to get to the
lightbulb.
In this episode a truckload of radioactive waste has been hijacked
and Charlie uses triangulation of the radiation the waste emits
to find where it is. This is mathematically similar to trying to find a
lightbulb in a very large field (without moving). If you are standing in
a field, then you will be able to see the lightbulb but you won't be able
to tell how far away it is. This means you know that it lies somewhere
on a particular line that goes through you, which probably wouldn't be
particularly useful, since to find the lightbulb without gathering more
information you would have to walk along the entire line to get to the
lightbulb. However, let's say you have a friend in the field and both
you and your friend have lightbulbs and radios. Then you can report to each
other the angle between the friend's lightbulb and the other lightbulb. Is
this enough to find the other lightbulb? Not quite, because there is no
angle-angle theorem in geometry. In other words, if you adapt coordinates
so that you are at the origin, then if you double the distances of the
other lightbulb and your friend from the origin, both the angles that you
and your friend measure will be the same. The only way to fix this is to
measure the distance between you and your friend.
However, let's say you have a friend in the field and both
you and your friend have lightbulbs and radios. Then you can report to each
other the angle between the friend's lightbulb and the other lightbulb. Is
this enough to find the other lightbulb? Not quite, because there is no
angle-angle theorem in geometry. In other words, if you adapt coordinates
so that you are at the origin, then if you double the distances of the
other lightbulb and your friend from the origin, both the angles that you
and your friend measure will be the same. The only way to fix this is to
measure the distance between you and your friend. Of course, if you are unlucky there will be a problem with this. There's
a chance that the lightbulb will lie on the line between you and your friend.
If this is the case, it would be impossible for you and your friend to
tell where on the line the lightbulb is. This can be fixed, however, by adding
a third friend. If the three friends make sure they aren't all standing on
a single line, then they can always find the lightbulb.
Of course, if you are unlucky there will be a problem with this. There's
a chance that the lightbulb will lie on the line between you and your friend.
If this is the case, it would be impossible for you and your friend to
tell where on the line the lightbulb is. This can be fixed, however, by adding
a third friend. If the three friends make sure they aren't all standing on
a single line, then they can always find the lightbulb.