Bernoulli Trials and Binomial Experiments (Continued)
| This lab is a continuation of the one from last lab. Recall terminology and notations we learned last time: |
| ||
Terminology
One Bernoulli Trial: an event with only two outcomes: failure and success
- We designate the probability of success with
p- Example
- one Bernoulli trial: tossing a fair coin once
Success: head Failure: tail
One Binomial Experiment: Consisting of a series of independent, identical Bernoulli Trials
-
nthe number of Bernoulli Trials in one experiment. -
pthe probability of success in each of the independent trials;premains the same from trial to trial. -
Xthe number of successes in one experiment.
- Example
- one Binomial experiment: tossing a fair coin 5 times.
-
n=5(there are5Bernoulli trials in the experiment) -
p=0.5(the probability for the coin to land on its head is half since it's a fair coin) -
X= the number of heads we get if we toss a fair coin5times.
-
Binomial Random Variable: X = the number of successes in one binomial experiment.
-
Xis called a Binomial Random Variable since it's used to describe the result of a Binomial Experiment. -
Xis a random variable since the outcome of each experiment is random,Xcan take on any value of0,1,2,...up ton. - The parameters for a Binomial Random Variable are (
n,p). - Distribution of
X:
| X | 0 | 1 | ... | k | ... | n |
| Probability | | | ... | | ... | |
- Binomial probability:
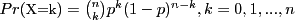 .
.
- Example
- An appropriate random variable for the above example is:
X= the number of heads we get in 5 tosses. The distribution ofXtells us the values of Pr(X=0),...,Pr(X=5). You can evaluate the distribution ofXby the binomial probability formula.
For instance,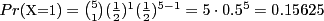
Histogram: a graphic summary of the observed distribution of a random variable.
-
Y- axis: the frequencies or relative frequencies -
X- axis: the observed outcomes of the variable.
Pattern: an important idea in descriptive statistics.
- Overall pattern includes notions about:
- shape (bell-shaped, multi-mode; symmetric, skewed)
- center (mean, median)
- spread (quartiles, standard deviation)
Assignment
- About 90% of newly manufactured computer chips work perfectly. The rest fail because of random impurities in the silicon. Suppose that quality control inspectors select 50 chips at random as they emerge from the manufacturing process, and test them.
- Explain why testing a chip can be considered a Bernoulli trial.
- Define a binomially distributed random variable
X, specifying the values ofnandp. - Create an approximation of this binomial distribution by running 20 simulations. Plot a histogram from the simulation. ‡.
- Describe the histogram.
- Suppose the standard medication given to people with a certain kind of skin rash has proven to be effective for 60% of the sufferers. Now a researcher thinks she has discovered a new and better treatment. She will test this new medication on 40 subjects.
- If the 40 subjects had been treated with the old medication, how many might have been cured? Define an appropriate random variable, run 20 simulations, and create a graph ‡ of the distribution. Describe the result and compare it to the one created above.
- How many patients would the new medication have to cure in order to really convince you that it is definitely more effective than the old treatment?
- We have examined several kinds of Bernoulli trials and binomial distributions: tossing coins, guessing on tests, quality control, medical experiments. Describe another real-life situation that involves Bernoulli trials and define an appropriate random variable. (You are not supposed to use examples from Lab 1 or Lab 2). Without using the computer, describe what you think the histogram from a simulation of this binomial distribution would look like.
Hand in
- Please print out the results marked with ‡
- Answer the questions posed.
- Hand in your completed assignment at the start of lab next week.
